Domestic Air Freight Australia
The Fastest way to move air freight Australia-Wide.

 Remote And Regional Air Freight Delivery Specialists
Remote And Regional Air Freight Delivery Specialists
Explore CargoMaster’s Domestic Air Freight Services Across Australia
Before you make a move, make it with CargoMaster. When urgency is non-negotiable, whether it’s sizable, weighty, or presents logistical challenges, trust CargoMaster to deliver fast and efficiently anywhere across Australia.
CargoMaster specialises in handling tricky, oversized, heavy, or out-of-hours air freight requirements. With 35 years of invaluable experience, CargoMaster possesses the expertise and know-how to ensure your cargo reaches its destination swiftly and cost-effectively.
Choose confidence; choose CargoMaster—one of Australia’s most seasoned and trusted air freight companies. Your urgent shipments deserve the reliability and efficiency that CargoMaster consistently provides.
Overview Air Freight Australia
 As the demand for efficient freight solutions continues to rise, domestic air freight in Australia emerges as a favored choice for freight forwarders and those with pressing shipping needs. Capitalising on the speed and convenience of air transport, CargoMaster facilitates seamless city-to-city freight movements, eliminating the wait associated with road or rail alternatives.
As the demand for efficient freight solutions continues to rise, domestic air freight in Australia emerges as a favored choice for freight forwarders and those with pressing shipping needs. Capitalising on the speed and convenience of air transport, CargoMaster facilitates seamless city-to-city freight movements, eliminating the wait associated with road or rail alternatives.
Selecting the right air freight partner is crucial for a smooth and efficient logistics experience. Esteemed companies like CargoMaster offer a diverse array of services, backed by experienced staff well-versed in all facets of air freight operations, export packing, and other critical aspects of air freight forwarding.
 Understanding the full spectrum of options is paramount for customers seeking efficient, reliable, and fast domestic air freight services in Australia. CargoMaster stands as a reputable choice, ensuring a seamless and secure transportation experience.
Understanding the full spectrum of options is paramount for customers seeking efficient, reliable, and fast domestic air freight services in Australia. CargoMaster stands as a reputable choice, ensuring a seamless and secure transportation experience.
In a broader context, air freight plays a pivotal role in the Australian freight landscape. Despite representing less than 0.1% of the total freight volume in 2019, approximately 1.6 million tonnes of international and domestic air cargo underscore its significance, with 75% of air cargo being international, making a substantial contribution to Australia’s economy.
According to the Bureau of Infrastructure, Transport, and Regional Economics (BITRE), air freight constituted 21% of total trade by value in international merchandise trade in 2014, amounting to over $130 billion in 2016–17. The trade values flowing through Sydney and Perth airports align with those shipped through the major ports of Botany and Fremantle.
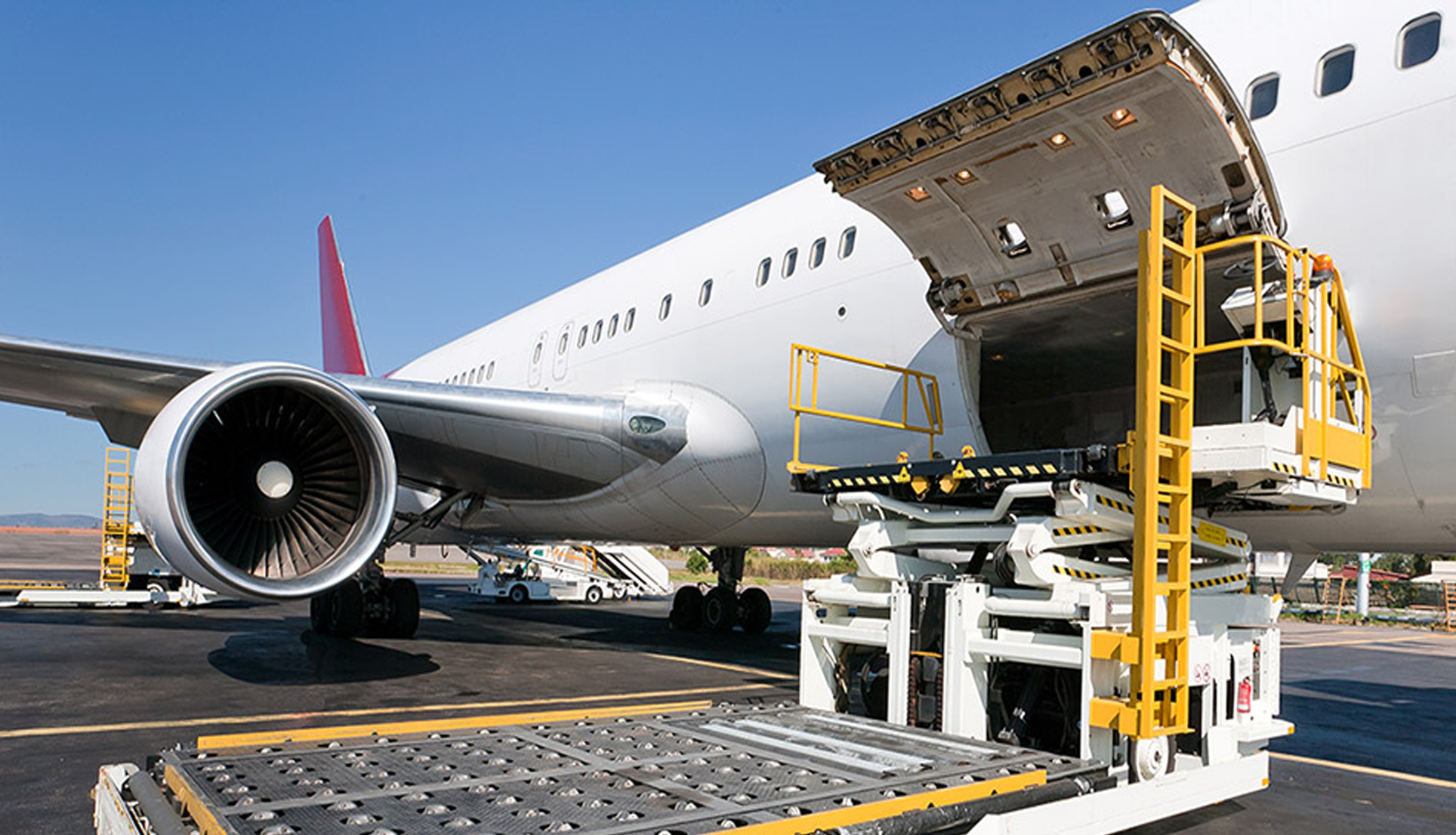 Recent studies by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) reveal the global value of air freight at a staggering $18.6 billion daily. The benefits extend beyond numbers, encompassing driving economic and social progress, providing access to global markets, generating trade, and fostering connections between nations. In this dynamic landscape, CargoMaster stands as a reliable partner, contributing to the seamless movement of goods both within Australia and on the global stage.
Recent studies by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) reveal the global value of air freight at a staggering $18.6 billion daily. The benefits extend beyond numbers, encompassing driving economic and social progress, providing access to global markets, generating trade, and fostering connections between nations. In this dynamic landscape, CargoMaster stands as a reliable partner, contributing to the seamless movement of goods both within Australia and on the global stage.
Discover the Growing Appeal of CargoMaster’s Domestic Air Freight Services in Australia
Discover the advantages of choosing CargoMaster for your urgent same-day interstate and overnight air freight needs throughout Australia.
Seasoned Professionals:
Benefit from genuine professionals boasting 35 years of experience, ready to assist with all your urgent domestic air freight requirements, including charters and deliveries to remote locations and mine sites equipped with a runway.
Extensive Transportation Resources:
When you choose CargoMaster, you align with an Australian domestic air freight company that provides real and substantial transportation resources to ensure your shipments are handled with expertise.
Proven Operator with Nationwide Reach:
CargoMaster stands as an established and proven air freight operator with a comprehensive air cargo network spanning Australia. No gimmicks, just reliable service without fast-talking salesmanship.
Door-to-Door 24/7 Service:
Enjoy fast and reliable door-to-door service 24/7 for your air freight needs across Australia, including regional and remote locations. CargoMaster specialises in mine-site deliveries, ensuring your cargo reaches its destination promptly.
Choose CargoMaster, where reliability, experience, and efficiency converge to provide you with unparalleled air freight solutions across the vast landscape of Australia.
Frequently Asked Questions by CargoMaster’s Customers
What does air freight mean?
Typically, air freight involves time-sensitive, fragile, or valuable cargo. In essence, it signifies the transportation of goods by aircraft.
What is domestic air freight?
Domestic air freight covers cargo uplifted anywhere in Australia destined for another location within the country, including Tasmania. International air freight either departs or arrives in Australia from another country.
How is air freight cost calculated?
Air freight is priced per kilogram or per cubic meter, whichever is higher. To determine costs, it’s crucial to establish whether your cargo is chargeable at actual weight or volumetric weight. Volumetric weight is calculated as length x width x height = (Total) x 167 or 250 (depending on your domestic air freight carrier). Contact CargoMaster for a Domestic Air Freight quote at TEL 1300 767 136.
What is the maximum weight for air freight?
Air freight size depends on factors such as aircraft size, consignment size, origin and destination, weight of the goods, and type of cargo. For specific information, it is best to consult with CargoMaster.
How much does it cost to move air freight?
The cost of air freight is determined by the weight or size of the consignment and is charged at a per kilogram rate. The type of cargo may also influence the cost of shipping air freight.
What can I send by air freight?
Most items can be sent via air freight, but it is advisable to contact CargoMaster first to ensure your consignment is not classified as hazardous or dangerous domestic air freight.
What type of air freight do you carry around Australia?
CargoMaster handles a diverse range of commodities, including machinery, medical equipment, ship spares, mining equipment, pallets, crates, construction machinery, industrial equipment, shop fittings, lighting, signage, tiles, and more.
Do you offer an Australia-wide DOOR TO DOOR air freight service?
Yes, CargoMaster provides a 24/7 DOOR TO DOOR or AIRPORT TO AIRPORT service to almost anywhere in Australia. Contact CargoMaster for Australia’s guaranteed best same-day air freight rates.
Can you provide any tips to help me get my domestic air freight moving quickly and smoothly?
Certainly! Ensure your air freight consignment is clearly addressed (with only one address!). If it is fragile, mark it as FRAGILE. If sending more than one piece, number each piece. Prepare your air freight for air transport with proper packaging and wrapping, ensuring it is clean and free of oil, dust, petrol, and other contaminants.
Experience Excellence with CargoMaster’s Domestic Air Freight Services Across Australia
In collaboration with a nationwide team of committed transportation professionals, CargoMaster stands out as a fully insured air freight specialist with an impressive 35 years of transportation experience. Renowned for delivering cost-effective air freight solutions, CargoMaster has successfully moved hundreds of consignments across Australia, catering to diverse cargo types.
CargoMaster offers you access to a proven and technologically advanced team of experienced professionals. With CargoMaster’s know-how, your goods are guaranteed to be uplifted and transported around Australia swiftly and cost-effectively. Trust in the expertise that comes with decades of successful operations in the air freight industry, as CargoMaster continues to save clients thousands of dollars in air freight and shipping costs.
CargoMaster Domestic Air Freight Destinations: Brisbane, Sydney, Melbourne, Perth, Adelaide, Darwin, Canberra, Gold Coast, Hobart
Welcome once again, and thank you for choosing CargoMaster. At CargoMaster, our focus is on providing exceptional service and user-friendly domestic air freight solutions. We comprehend the dynamic landscape of high-priority air freight and shipping, collaborating closely with our clients to ensure every consignment is delivered promptly, in optimal condition, and to the right destination—all at a competitive price!
CargoMaster is dedicated to delivering cost-effective solutions, offering both air and sea freight options to our clients. As an Australian Freight Forwarder with a reach extending across the nation and worldwide, CargoMaster serves major cities including Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, Hobart, Canberra, Darwin, and various regional centers. Trust CargoMaster for a seamless and efficient experience in the world of domestic air freight.
Addition Information (Click the + plus symbol to expand)
AUSTRALIAN AIRPORT CODES
| City | Country | Airport code |
|---|---|---|
| Adelaide | Australia | ADL |
| Brisbane | Australia | BNE |
| Cairns | Australia | CNS |
| Canberra | Australia | CBR |
| Gold Coast | Australia | OOL |
| Hobart | Australia | HBA |
| Melbourne | Australia | MEL |
| Perth | Australia | PER |
| Townsville | Australia | TSV |
| Mackay | Australia | MKY |
| Sydney | Australia | SYD |
| Karratha | Australia | KTA |
| Kununurra | Australia | KNX |
| Broome | Australia | BME |
| Rockhampton | Australia | ROK |
| Kalgoorlie | Australia | KGI |
| Port Hedland | Australia | PHE |
| Darwin | Australia | DRW |
| Alice Springs | Australia | ASP |
| Launceston | Australia | LST |
| Newman | Australia | ZNE |
| Maroochydore | Australia | MCY |
HAZARD LABELS DANGEROUS GOODS (DG)
Hazard Labels for
Dangerous Goods (DG)
The international community has established a classification system for easy identification of dangerous goods. These goods fall into nine primary classes, and some classes are further divided to address specific risks. Each class/division has a corresponding label that accurately represents the nature of the hazard. These labels must be attached to the package during transport and remain intact throughout the journey. Take a look at the illustrated examples below to understand how these labels effectively communicate the potential dangers.
Under regulations, labels must be clearly visible on the outside of the package and must stay on the package while in transit.
You can often find labels printed on most inner packages such as:
- aerosol cans
- bottles of bleach
- containers of thinners
- tins of paint
- many other products which are available at supermarkets and hardware stores.
Below are the 9 hazard labels for the 9 classes of dangerous goods.
Class 1 Explosives

This includes items such as:
- explosive substances
- pyrotechnic devices
- ammunition
- fireworks
- detonators.
Class 2 Gases

These can be transported as:
- compressed
- liquefied
- refrigerated liquefied
- gas in solution.
This includes aerosols. Class 2 has 3 divisions:
- Division 2.1 - flammable gases such as:
- butane
- propane
- Division 2.2 - non-flammable, non-toxic gases such as:
- oxygen
- liquid nitrogen
- compressed air
- Division 2.3 - toxic gases such as:
- chlorine
- hydrogen sulphide.
Class 3 Flammable liquids

This includes liquids with a boiling point of 35⁰ C or less, or a flash point of 60⁰ C or less such as:
- petrol
- alcohol
- perfumes
- essential oils
- hand sanitiser
- paints.
Class 4 Flammable solids

These are substances that can spontaneously combust and substances, that when they come into contact with water or emit flammable gases. Class 4 has 3 divisions:
- Division 4.1 - flammable solids such as:
- hexamine solid fuel tablets for camping stoves
- self-reactive substances
- desensitised explosives
- Division 4.2 - substances that can spontaneously combust under normal air transport conditions include:
- camphor
- sulphur
- matches
- Division 4.3 - substances that emit flammable gases when they come into contact with water include:
- sodium
- zinc particles
- activated carbon.
Class 5 Oxidising substances and organic peroxides

These substances are not necessarily combustible on their own but can react dangerously with other substances. Class 5 has 2 divisions:
- Division 5.1 - oxidising substances that may not be necessarily combustible, but they may readily yield oxygen and cause other materials to combust, such as:
- hydrogen peroxide
- ammonium nitrate
- potassium chlorate
- sodium nitrate
- Division 5.2 - organic peroxides are thermally unstable and can emit heat and give off harmful or flammable vapours. They can also be liable to explosive decomposition and react dangerously with other substances. Examples are:
- acetyl acetone peroxide
- benzoyl peroxide
- peracetic acid.
Class 6 Toxic and infectious substances

These substances can cause sickness, injury or death if consumed. Class 6 has 2 divisions:
- Division 6.1 - toxic substances that can cause death, injury or to harm human health if swallowed, inhaled or by skin contact, such as:
- chloroform
- arsenics
- cyanides
- cytotoxic waste
- barium compounds
- pesticides
- Division 6.2 - infectious substances that contain or are expected to contain pathogens that can cause disease in humans or animals, including:
- medical or clinical waste
- patient specimens
- genetically modified organisms
- infectious substances
- infected animals.
Class 7 Radioactive materials

These are substances that emit invisible ionising radiation that can be harmful to humans and animals. It can cause objects such as aircraft and equipment to become contaminated if not packaged and handled correctly, such as:
- uranium
- radioactive ores
- isotypes
- radium
- cesium
- x-ray equipment
- medical equipment or parts.
Class 8 Corrosives

These substances can cause irreversible damage if they come into contact with skin and could destroy other freight, or materially damage containers or aircraft. This includes:
- acids
- corrosive cleaners
- battery fluid
- formaldehyde
- hydrofluoric acid.
Class 9 Miscellaneous
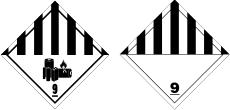
These are substances and articles which, during air transport, present a danger not covered by other classes. There are 2 types of handling labels – 1 for lithium battery shipments, and another for all other miscellaneous dangerous goods. This class includes:
- lithium batteries
- battery powered vehicles
- battery powered equipment
- first aid kids
- environmentally hazardous substances
- dry ice
- magnetised materials
- asbestos.
Handling labels
In addition to hazard labels, trained staff must attach handling labels where needed. Staff must use these 4 handling labels with the appropriate hazard labels:
Cargo aircraft only

This label is used to show that the load cannot be carried on a passenger aircraft.
Cyrogenics

This label is used on liquefied gases, such as the ones in Class 2.
This way up

This label ensures a load is placed the correct way up and can be used for non-dangerous goods.
Magnetised material

This label ensures that the load is kept away from the aircraft compass detector unit while being loaded and unloaded.
HIDDEN DANGEROUS AIR CARGO
Please Note: The below list does not describe all types of hazardous air cargo (it is not exhaustive and all encompassing). General items listed below may be found in baggage and possibly have hazards that are not immediately apparent. There are strict laws in relation to lodging of hazardous air cargo and compliance with hazardous air cargo regulations.
Typical examples of hazardous air cargo
Engines (contain fuel and that are not cleaned, purged and sealed)
Mining equipment
Magnets
Pressurised containers
Passenger baggage (containing flammable gas or liquid lighter refuel. camping stove cylinders
Photographic Supplies
Expeditionary equipment
Vaccines
Solvents, adhesives
Pesticides
Dental apparatus
Machinery parts
Frozen foods (packed in solid dry ice)
Dry Ice
Tool Boxes (compressed gases, aerosols)
Electrical equipment
Diving equipment
Pharmaceuticals
Switches in electrical equipment
Toys (made of cellulose)
Refrigerators (may contain gases or chemicals)
Swimming pool chemicals
Pressurised containers
Engines (contain fuel and that are not cleaned, purged and sealed)
Mining equipment
Diagnostic specimens
Thermometers (containing mercury)
Frozen Embryos
Ammunition
Swimming pool chemicals
Aerosols
Compressed non-flammable gas
Batteries
Breathing Apparatus
Frozen foods (packed in solid dry ice)
Motor Vehicle parts
Chemicals
IATA AIRPORT CODES AUSTRALIA
Sydney Airport – SYD
Melbourne Airport – MEL
Brisbane Airport – BNE
Perth Airport – PER
Adelaide Airport – ADL
Gold Coast Airport – OOL
Cairns Airport – CNS
Canberra Airport – CBR
Hobart Airport – HBA
Darwin Airport – DRW
Townsville Airport – TSW
Newcastle Airport – NTL
Sunshine Coast Airport – MCY
Mackay Airport – MKY
Avalon Airport – AVV
Alice Springs Airport – ASP
Rockhampton Airport – ROK
Ballina Airport – BNK
Ayers Rock Airport – AYQ
Karratha Airport – KTA
Hamilton Island Airport – HTI
Proserpine Airport – PPP
Broome Airport – BME
Coffs Harbour Airport – CFS
Port Hedland Airport – PHE
Newman Airport – ZNE
Kalgoorlie-Boulder Airport – KGI
Albury Airport – ABX
Gladstone Airport – GLT
Mildura Airport – MQL
Port Macquarie Airport – PQQ
Mount Isa Airport – ISA
Dubbo Airport – DBO
DGR SIGNIFICANT CHANGES AND AMENDMENTS (59th Edition) 2018
SIGNIFICANT CHANGES AND AMENDMENTS TO THE 59TH EDITION (2018)
The 59th edition of the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations incorporates all amendments made by the IATA Dangerous Goods Board and includes addenda issued by ICAO to the 2017–2018 edition of the Technical Instructions. The following list is intended to assist the user to identify the main changes introduced in this edition and must not be considered an exhaustive listing. The changes have been prefaced by the section or subsection in which the change occurs. 2—Limitations 2.3—Dangerous Goods Carried by Passengers or Crew 2.3.5.9—Limitations have been adopted on the number of portable electronic devices (PED) and the number of spare batteries for the PED that may be carried by passengers or crew. The limit is a maximum of 15 PED and a maximum of 20 spare batteries. These maximums may be exceeded with the approval of the operator. Table 2.3.A has also been revised to reflect these limits. 2.8—Operator Variations There are a number of additions, deletions and amendments to variations submitted by operators. 3—Classification 3.9.2—This subsection has been restructured to bring in all substances and articles that are assigned to Class 9 with their respective UN numbers and proper shipping names. The substances and articles have then been grouped according to the hazard they pose in transport. 4—Identification 4.4—Special Provisions A70—Which identifies the conditions under which engines may be considered as “not restricted”. The conditions have been revised to require that the shipper provide written or electronic documentation stating that a flushing and purging procedure for flammable liquid powered engines has been followed. A203—Identifies that vehicles powered by an engine powered by both a flammable liquid and flammable gas must be assigned to the entry Vehicle, flammable gas powered. The special provision has been revised to clarify that in this instance the applicable provisions of PI 950(a) must also be met. 5—Packing 5.0.1.5.1—Has been revised to include new restrictions on packages containing lithium batteries, UN 3090 and UN 3480 only, being placed into an overpack with packages containing dangerous goods classified in Class 1 other than Division 1.4S, Division 2.1, Class 3, Division 4.1 or Division 5.1. 5.0.2.11—An additional note has been added to identify that lithium batteries, UN 3090 and UN 3480 only, are not permitted in the same outer packaging with dangerous goods classified in Class 1 other than Division 1.4S, Division 2.1, Class 3, Division 4.1 or Division 5.1. Packing Instructions PI 951—Has been revised to include a requirement that if the vehicle is powered by an engine using both flammable gas and flammable liquid fuels, then the shipper must also meet the relevant provisions of PI 950. PI Y960—A note has been added to reinforce that dangerous goods in PG I are not permitted. PI 965 and PI 968—Text has been added to identify the restrictions on packing lithium batteries (UN 3480 and UN 3090 only) in the same outer packaging with dangerous goods classified in Class 1 other than Division 1.4S, Division 2.1, Class 3, Division 4.1 or Division 5.1. There are also restriction on placing packages containing lithium batteries (UN 3090 and UN 3480 only) into an overpack with packages containing dangerous goods classified in Class 1 other than Division 1.4S, Division 2.1, Class 3, Division 4.1 or Division 5.1. These restrictions apply to Section IA and IB. For Section II, cells and batteries must not be packed in the same outer packaging with other dangerous goods. 7—Marking & Labelling 7.1.5.5.2—Text has been added recommending that the UN number(s) on the lithium battery mark be of a minimum size.
9—Handling 9.3.2—Table 9.3.A and the provisions of 9.3.2 have been revised to introduce segregation requirements for lithium batteries (UN 3480 and UN 3090 only) and dangerous goods classified in Class 1 other than Division 1.4S, Division 2.1, Class 3, Division 4.1 or Division 5.1. This aligns to the changes in 5.0.1.5, 5.0.2.11, PI 965 and PI 968. A note has been added to identify that the segregation of packages and overpacks loaded into ULD and aircraft cargo compartments, while recommended as of 1 January 2018, will not become mandatory until 1 January 2019. Appendix B—In Appendix B.2.2.4 new Cargo IMP codes have been added for UN 3090, Section IA and IB of PI 968—RBM and UN 3480, Section IA and IB of PI 965—RBI. These two new IMP codes facilitate the differentiation of fully regulated lithium batteries (UN 3090 and UN 3480) from those packed with equipment or contained in equipment (UN 3091 and UN 3481), which are currently assigned to RLM and RLI respectively. Appendix D—contact details for competent authorities have been updated. Appendix E—changes have been made to the list of UN Specification Packaging Suppliers (E.1) and the Package Testing Facilities (E.2). Appendix F—the list of Sales Agents (F.2), IATA Accredited Training Schools (F.3—F.5) and IATA Authorised Training Centres (F.6) have been revised. Appendix I—A new appendix has been added to this edition of the DGR to provide the detail of the changes that will come into effect as of 1 January 2019 based on the adoption of the changes arising from the 20th revised edition of the UN Model Regulations as well as the changes that have been agreed to date by the ICAO Dangerous Goods Panel for inclusion into the 2019–2020 edition of the Technical Instructions. These changes include: ● replacement of most instances of the word “risk” by the word “hazard”. The changes reflects the increasing use of safety management systems where “risk” is the likelihood of an event combined with the severity of the outcome, whereas hazard is used to identify the inherent properties. So, for example a substance may have a “subsidiary hazard”, not a “subsidiary risk”. ● significant changes to the provisions for the classification of corrosive substances. These changes reflect the work of the UN Subcommittee with the GHS Subcommittee to better align the classification provisions for transport for Class 8 substances with those for supply and use. ● a new requirement for manufacturers and subsequent distributors of lithium cells or batteries to make available a summary of the UN 38.3 tests. ● new provisions for the classification of articles containing dangerous goods, n.o.s.. This includes twelve new UN numbers, UN 3537 to UN 3548, that have been assigned to articles containing dangerous goods in Classes 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 and 9 and Division 6.1. The details of the provisions that will come into effect in 2019 for air transport have still to be finalised by the ICAO dangerous Goods Panel. ● a number of new and modified special provisions. ● removal of the lithium battery handling label (7.2.4.7). As of 1 January 2019 only the lithium battery mark (7.1.5.5) will be permitted on packages of lithium batteries prepared in accordance with Section IB of PI 965 or PI 968, or Section II of PI 965 to PI 970. REFERENCE MARKS The following symbols placed against an item indicate changes from the previous edition: Symbol—Meaning —Addition of a new item. —Change to an item. —Cancellation of an item. —Additional IATA requirements. —Indicates that the item relates entirely to Radioactive shipments
AIR FREIGHT AUSTRALIA DOMESTIC AIRLINES
| Airline | Airline Code | Customer Service | Sales Office | Website | |
 | TL | 1800 627 474 | 1800 627 474 | http://www.airnorth.com.au/ | |
 | 1300 780 970 | 1300 780 970 | http://www.allianceairlines.com.au/ | ||
 | JQ | 13 15 38 | +61 3 9645 5999 | http://www.jetstar.com | |
 | QF | 13 13 13 | http://www.qantas.com.au | ||
 | ZL | 13 17 13 | http://www.regionalexpress.com.au | ||
 | VA | 13 67 89 | http://www.virginaustralia.com | ||
| Provider | Website | ||||
| Swissport Australia | www.swissport.com | ||||
| Air Menzies International (AMI) | https://airmenzies.com/ | ||||
| Patrick Air Services | http://w.auww.patrick.com | ||||
| Qantas Airways (passenger & ramp handling) | http://www.qantas.com.au | ||||
| Toll Dnata | http://www.tolldnata.com | ||||
UNIT LOAD DEVICES (ULD)
ULDs are considered an aircraft part and are the only aircraft parts that can be removed from the aircraft and be returned after being handled by unregulated operators, ULD's are considered to directly contribute to flight safety.
Types of Unit Load Devices Used in Australia
AKE Container
- Type: AKE CONTAINERATA Code: LD3
- Internal Volume: 152 cu. ft. 4.3 mc
- Weight Limit: 1,588 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F, 777, Airbus
 AAU Container
AAU Container
- Type: AAU CONTAINER
- ATA Code: LD29
- Internal Volume: 505 cu. ft. 14.3 mc
- Weight Limit: 4,626 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F
 ALF Container
ALF Container
- Type: ALF CONTAINER
- ATA Code: LD6
- Internal Volume: 310 cu. ft. 8.78 mc
- Weight Limit: 3,175 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F,777, Airbus
 AMA Container
AMA Container
- Type: AMA CONTAINER
- ATA Code: M1
- Internal Volume: 621 cu. ft. 17.58 mc
- Weight Limit: 6,804 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747F
 AMF Container
AMF Container
- Type: AMF CONTAINER
- Internal Volume: 516 cu. ft. 14.6 mc
- Weight Limit: 5,035 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747,747F, 777, Airbus
P1P_PAG Pallet
- Type: P1P, PAG PALLET
- Size:
- Base: 88″x 125″
- Height: 64″, x 96″,118″
- Weight Limit: 4,626kg
(LD),6,033kg (MD) - Loadable Aircraft Type: 747,747F, 777, Airbus
 PEB Container
PEB Container
- Type: PEB CONTAINER
- Size:
- Base: 53″ x 88″
- Height: 84″
- Weight Limit: 1,800kg
(B-HIH -1,300 KG) - Loadable Aircraft Type: 747F
 PLA Pallet
PLA Pallet
- Type: PLA PALLET
- Size:
- Base: 60.4″x 125″
- Height: 64″
- Weight Limit: 3,175kg
Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F, 777, Airbus
 PMC_PQP_P6P Pallet
PMC_PQP_P6P Pallet
- Type: PMC, PQP, P6P PALLET
- Size: Base: 96″ x 125″
- Weight Limit: 5,035 kg (LD), 6,804 kg (MD)
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F, 777, Airbus
 RKN Container
RKN Container
- Type: RKN CONTAINER
- ATA Code: LD3
- Internal Volume: 125.41 cu. ft. 3.55 mc
- Weight Limit: Weight: 1,588 kg
- Loadable Aircraft Type: 747, 747F, 777, Airbus
 VZA_VRA
VZA_VRA
- Size: Fitted on PGA 20 ft. Pallet
- Max Width for Lower Car: 81″/ 205 cm
- Max Centre Height for Lower Car: 59″/ 150 cm
- Max Wheel Base: 312 cm
- Weight Limit: 2,500 kg(Upper Car)
9,300 kg c(Max Gross Weight of Pallet) - Loadable Aircraft Type: 747F Upper Deck
AIR FREIGHT FREIGHTER SPECIFICATIONS
| Make/Model | Max Payload Tonnes | Max Loadable Volume CBM3 | Cargo Hold Dims LxWxH cm | Cargo Door Size WxH cm |
| Cessna 406 Titan | 1.2 | 6.5 | 320 x 120 x 117 | 124 x 116 |
| Fairchild Metroliner II | 1.4 | 12 | 835 x 115 x 120 | 130 x 115 |
| Fairchild Metroliner III | 2.1 | 12 | 775 x 158 x 145 | 130 x 115 |
| Fairchild Metroliner 23 | 2.3 | 18 | 775 x 158 x 145 | 127 x 115 |
| Falcon 20 / 200 | 2.5 | 11 | 704 x 156 x 142 | 190 x 140 |
| Shorts 360 | 3.5 | 40 | 815 x 190 x 190 | 142 x 168 |
| Saab 340 | 3.8 | 40 | 1300 x 170 x 170 | 135 x 130 |
| Aerospatiale ATR42 | 4.6 | 40 | 1080 x 225 x 143 | 125 x 153 |
| Fokker 27 | 6.3 | 58 | 1336 x 210 x 190 | 228 x 175 |
| Antonov AN-26 | 6.5 | 45 | 1110 x 220 x 160 | 230 x 171 |
| Antonov AN-74 | 6.5 | 45 | 1000 x 215 x 220 | 226 x 220 |
| British Aerospace ATP | 8.2 | 78 | 1500 x 195 x 180 | 250 x 169 |
| Lockheed L-188 Electra | 15 | 135 | 2000 x 280 x 220 | 355 x 203 |
| Boeing 737-300F | 16 | 115 | 2100 x 310 x 220 | 340 x 215 |
| Antonov AN-12 | 18 | 95 | 1380 x 300 x 250 | 300 x 250 |
| Lockheed L-100 Hercules | 21 | 140 | 1707 x 302 x 274 | 302 x 274 |
| Boeing 727-200F | 23.5 | 144 | 2712 x 351 x 218 | 340 x 218 |
| Boeing 757F | 39 | 187 | 3327 x 353 x 218 | 340 x 218 |
| Airbus A300 B4F | 40 | 280 | 3900 x 477 x 223 | 358 x 256 |
| Douglas DC8-62 | 40 | 200 | 3400 x 317 x 203 | 355 x 215 |
| Douglas DC8-54/55 | 41 | 180 | 3100 x 317 x 203 | 355 x 215 |
| Ilyushin IL-76 | 45 | 180 | 1850 x 345 x 325 | 344 x 340 |
| Antonov AN-22 | 50 | 650 | 2640 x 430 x 430 | 430 x 430 |
| Lockheed L10-11 Tristar | 55 | 420 | 3300 x 360 x 274 | 431 x 284 |
| Boeing 767-300F | 55 | 400 | 3000 x 400 x 250 | 340 x 254 |
| Douglas DC10-30 | 65 | 400 | 3725 x 448 x 245 | 350 x 245 |
| McDonnell Douglas MD11 | 85 | 500 | 4800 x 350 x 245 | 355 x 245 |
| Boeing 747-100F | 90 | 675 | 4800 x 488 x 300 | 340 x 300 |
| Boeing 747-200F | 100 | 675 | 4900 x 488 x 300 | 340 x 300 |
| Boeing 777F | 100 | 625 | 4400 x 488 x 300 | 372 x 305 |
| Boeing 747-300/400F | 110 | 675 | 5000 x 488 x 300 | 340 x 300 |
| Antonov AN-124 | 120 | 800 | 3650 x 640 x 440 | 640 x 440 |
| Antonov AN-225 | 250 | 1100 | 4300 x 640 x 440 | 640 x 440 |
INCOTERMS
INCOTERMS are standard trade terms most commonly used in international freight contracts for sale of goods. It is essential that you are aware of your terms of trade prior to shipment.
EXW – EX WORKS (… named place of delivery)
The Seller’s only responsibility is to make the goods available at the Seller’s premises. The Buyer bears full costs and risks of moving the goods from there to destination.
FCA – FREE CARRIER (… named place of delivery)
The Seller delivers the goods, cleared for export, to the carrier selected by the Buyer. The Seller loads the goods if the carrier pickup is at the Seller’s premises. From that point, the Buyer bears the costs and risks of moving the goods to destination.
CPT – CARRIAGE PAID TO (… named place of destination)
The Seller pays for moving the goods to destination. From the time the goods are transferred to the first carrier, the Buyer bears the risks of loss or damage.
CIP– CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO (… named place of destination)
The Seller pays for moving the goods to destination. From the time the goods are transferred to the first carrier, the Buyer bears the risks of loss or damage. The Seller, however, purchases the cargo insurance.
DAT – DELIVERED AT TERMINAL (… named terminal at port or place of destination)
The Seller delivers when the goods, once unloaded from the arriving means of transport, are placed at the Buyer’s disposal at a named terminal at the named port or place of destination. “Terminal” includes any place, whether covered or not, such as a quay, warehouse, container yard or road, rail or air cargo terminal. The Seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to and unloading them at the terminal at the named port or place of destination.
DAP – DELIVERED AT PLACE (… named place of destination)
The Seller delivers when the goods are placed at the Buyer’s disposal on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the names place of destination. The Seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to the named place.
DDP – DELIVERED DUTY PAID (… named place)
The Seller delivers the goods -cleared for import – to the Buyer at destination. The Seller bears all costs and risks of moving the goods to destination, including the payment of Customs duties and taxes.
MARITIME TERMS
FAS – FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP (… named port of shipment)
The Seller delivers the goods to the origin port. From that point, the Buyer bears all costs and risks of loss or damage.
FOB– FREE ON BOARD (… named port of shipment)
The Seller delivers the goods on board the ship and clears the goods for export. From that point, the Buyer bears all costs and risks of loss or damage.
CFR– COST AND FREIGHT (… named port of destination)
The Seller clears the goods for export and pays the costs of moving the goods to destination. The Buyer bears all risks of loss or damage.
CIF – COST INSURANCE AND FREIGHT (… named port of destination)
The Seller clears the goods for export and pays the costs of moving the goods to the port of destination. The Buyer bears all risks of loss or damage. The Seller, however, purchases the cargo insurance.
SAVE MONEY, SAVE TIME with CargoMasters’ Domestic Air Freight Services.
At CargoMaster we strive to deliver cost effective freight forwarding services to business, government and private individuals.
Contact our team today CargoMaster will save you too!
[email protected]
1300 767 136
Contact Us Now! … With CargoMaster, we can Save you More!
Thank-you for contacting us, we appreciate the opportunity, if your shipment relates to air freight or less than a container load sea freight, please include the weight and dimensions of each piece in your request. We look forward to working with you, please feel free to call at any time.




